Iliotibial Band (ITB) Friction Syndrome | Leg Injury
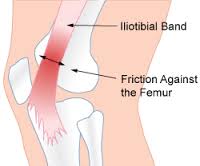
ITB is an abbreviation for the “iliotibial band” which is a strong, flat tendon-like structure which connects the muscles of the hip to the outside of the lower leg. Friction occurs as the lower part of the ITB rubs over the lateral femoral epicondyle. If the ITB is tight and the rubbing becomes repetitive, increased friction will result causing irritation of the band and the bursa (a fluid filled sac) which sits between the band and the underlying surface. The band often rubs over the bony prominence at around 30 degrees of knee flexion.
ITB is an abbreviation for the “iliotibial band” which is a strong, flat tendon-like structure which connects the muscles of the hip to the outside of the lower leg. Friction occurs as the lower part of the ITB rubs over the lateral femoral epicondyle. If the ITB is tight and the rubbing becomes repetitive, increased friction will result causing irritation of the band and the bursa (a fluid filled sac) which sits between the band and the underlying surface. The band often rubs over the bony prominence at around 30 degrees of knee flexion.
Who is affected by ITB friction syndrome?
ITB friction syndrome is very common in runners (both novice and elite) and becomes prominent after an increase in training volume. There are both modifiable and non- modifiable factors that can lead to this condition.
MODIFIABLE
- Footwear
- Training Volume
- Excessive downhill running
- Weak hip muscles
- Tight hip muscles
- Excessive Foot Pronation (flattening)
NON-MODIFIABLE
- Naturally thick ITB
- Naturally tight ITB
- Prominent lateral femoral epicondyle
- Increased Q angle (related to shape of the pelvis)
- Symptoms of ITB Friction Syndrome includes
- Pain at the outside of the knee
- Pain with exercise especially running and riding
- Pain with stairs (especially coming down)
- A “snapping” or “catching” sensation of the knee
Advanced Physio treatment
Advanced Physio uses a combination of treatments dependent on the severity of the injury. We recommend initially treating the injury using Advanced Physio’s manual therapy, exercise prescription in combination with:
- Rest from aggravating activity
- Ice the area
- Anti-inflammatory medication, as directed by referring doctor
Our physiotherapy treatment will be customised to suit the patient and may include:
- Stretching of hip muscles (gluteus maximus and tensa fascia latae especially)
- Strengthening of hip abductor muscles
- Stretching of the ITB
- Foot wear modification (if required)
- Orthotics (if required)
- Gait analysis and correction